What if a doctor were able to examine a patient thoroughly during a tele-health consultation?
What if a surgeon could remotely operate on a patient? What if you could touch a loved one during a video call? This may all be very possible with the help of haptic technology.
What is Haptic Technology?
Derived form the Greek word ‘touch’, at its most basic, haptic means anything relating to the sense of touch. In scientific and technological terms however, haptics is the transmitting and understanding information through the sense of touch. Some form of haptics that you would be familiar with is the vibration in a mobile phone or the rumble in a game controller. While more complicated forms of haptic tech can be found in a range of wearables, AR/VR experiences, digital out-of-home advertising, automotive infotainment and high-end military and industrial simulation equipment.

Haptic technology is around the corner
Now while sharing a hug with your international friend may still be a bit far off. Dr Do, Scientia Lecturer and UNSW Medical Robotics Lab director estimate the new technology to become available in the next 18 months to three years – if plans to commercialise the device are realised. Dr Do says the sense of touch is something many people take for granted to perform everyday tasks. “When we do things with our hands, such as holding a mobile phone or typing on a keyboard, all of these actions are impossible without haptics,” he said.
Dr Do and his team have invented a wearable haptic glove. A three-way directional skin stretch device (SSD), built into the fingertips of the wearable haptic glove we also created, is like wearing a second skin – it’s soft, stretchable and mimics the sense of touch – and will enable new forms of haptic communication to enhance everyday activities.
“Unlike existing haptic devices, our technology is soft, lightweight, and thin and therefore, we hope users will be able to integrate it into what they’re wearing to provide realistic haptic experiences in settings including rehabilitation, education, training and recreation,” he said.
The technology could enable a user to feel objects inside a virtual world or at a distance; for example, a scientist could feel a virtual rock from another planet without leaving their lab, or a surgeon could feel a patient’s organ tissues with surgical tools without directly touching them.
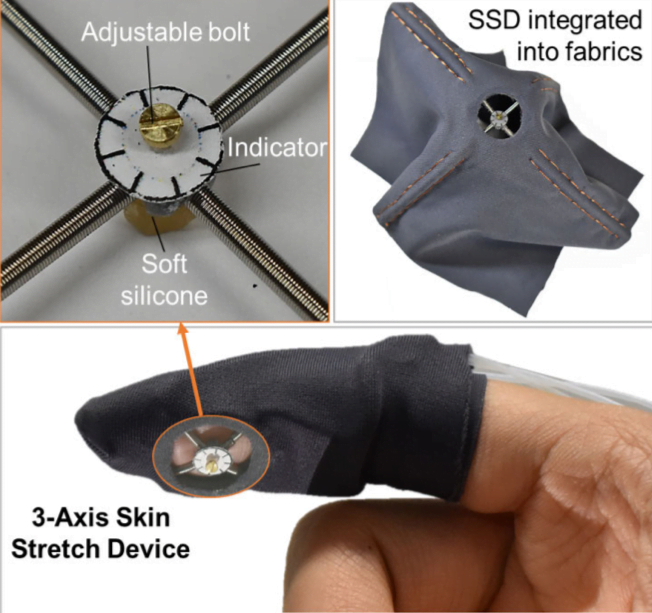

How it works
The new technology overcame issues with existing haptic devices by introducing a novel method to recreate an effective haptic sensation via soft, miniature artificial “muscles”. The wearable haptic glove enables people to feel virtual or remote objects in a more realistic and immersive way. The inbuilt soft artificial muscles generate sufficient normal and shear forces to the user’s fingertips via a soft tactor, enabling them to effectively reproduce the sense of touch.
Dr Do explains: “Imagine you are in Australia while your friend is in the United States. You wear a haptic glove with our integrated three-way directional SSDs in the fingertips and your friend also wears a glove with integrated 3D force sensors.If your friend picks up an object, it will physically press against their fingers and their glove with 3D force sensors will measure these interactions. These 3D force signals are sent to your haptic glove, then the integrated three-way directional SSDs will generate these exact 3D forces at your fingertips, enabling you to experience the same sense of touch as your friend.”
Why Haptic Technology needs to improve
Dr Do says the ability to effectively reproduce the sense of touch via the new wearable haptic device would have a wide range of benefits; for example, during today’s COVID-19 pandemic when people were relying on video calls to stay connected with loved ones. Dr Do’s team plan to implement the device in various haptic applications such as haptic motion guidance, navigational assistance for older people and those with low vision, tactile textual language, and 3D force feedback display for use in surgical robots, prosthesis and virtual and augmented reality.
Click here if you wish to find out more about the SSD and read more on the topic of Haptic Technology.

